Market Trends of Cloud Robotics Industry
This section covers the major market trends shaping the Cloud Robotics Market according to our research experts:
Rising Demand for Industrial Robotics to Augment the Market Growth
- With the development of cloud computing, big data, and other emerging technologies, the integration of cloud technology and robotic systems allows for designing multi-robot systems with high performance and high complexity. Growing penetration of the IoT and investments in robotics have been the major contributors to the growth of industrial robotics.
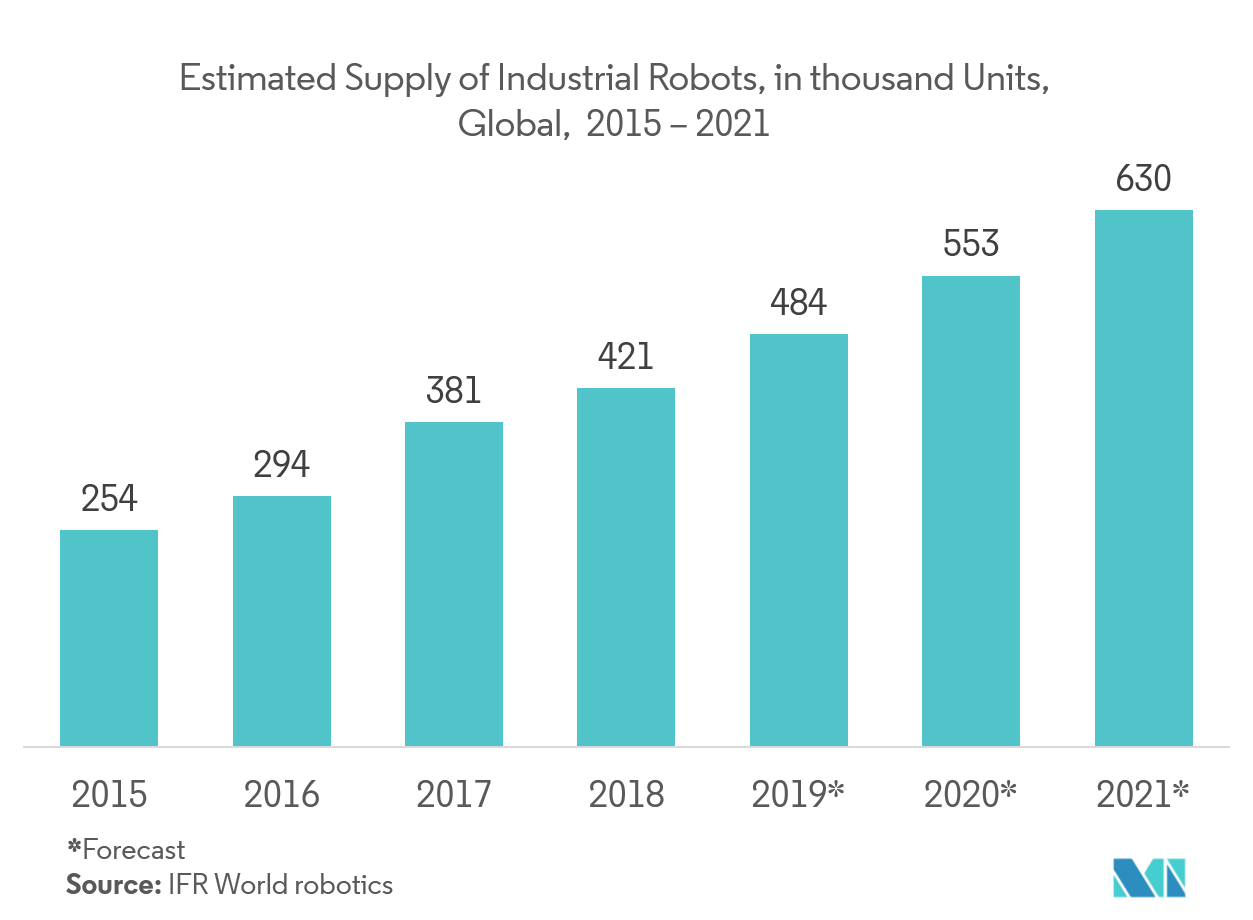
- According to the International Federation of Robotics, robot installations worldwide have recovered rapidly, making 2021 the most successful year in the robotics industry's history (IFR). "Demand reached high levels across industries due to the ongoing trend toward automation and continued technological innovation." Even the pre-pandemic record of 422,000 installations per year in 2018 was broken in 2021."
- Furthermore, Industrial robot sales have made a significant comeback. A new high of 486,800 units was shipped globally, a 27% increase over the previous year. Asia/Australia witnessed the greatest increase in demand, with installations increasing 33% to 354,500 units. With 49,400 units sold, the Americas climbed by 27%. With 78,000 units installed, Europe had a double-digit increase of 15%.
- Industrial robotics have been witnessing a huge demand over the past decade, owing to the adoption of smart factory systems. With the development of industrial robots, programmed robots have reached high-performance levels in real-time applications, accuracy, robustness, and compatibility.
- The availability of small-capacity and cost-effective solutions from small-and medium-sized industries is influencing the adoption of industrial automation. Apart from this, connecting robots, machines, and automation equipment to the cloud allow manufacturers to unlock the highest levels of performance and uptime from their automation systems.
Asia-Pacific to Witness a Significant Growth
- The market in Asia-Pacific is driven by the growing penetration of cloud computing, coupled with the incorporation of robotics and automation among the end-users. The automation adoption rate in this region, especially in China, India, and Japan, is the highest globally.
- China is the biggest spender on public cloud in the Asia-Pacific region. The local IaaS market is the first choice for small- and medium-enterprises for IT resources construction in games, video, and mobile internet.
- Industrial robots are predicted to increase rapidly in China as the downstream manufacturing sector recovers and the production of lithium batteries, new energy vehicles, and other industries expand.
- For the past eight years, China has been the world's largest market for industrial robots. According to a five-year plan released by the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, China's robotics industry's operating revenue is predicted to rise at a 20 percent annual pace from 2021 to 2025.
- The growing demand for advanced automotive manufacturing drives robotics partnerships between the United States and Chinese companies. This may help China advance cloud services, which will likely further develop the Asia-Pacific cloud robotics market.
- The key players in this region are investing in developing robotic cloud solutions. For instance, In April 2021, CloudMinds Technology Inc. announced a Series B+ round of funding totaling more than USD 153 million. According to the Shanghai-based service robotics company, it will continue to develop humanoid models for residential use.
- It also stated that CloudMinds develops service robots for retail, education, healthcare, and hospitality that employ cloud computing. Its products include the wheeled humanoid XR-1 Service Robot, the Cloud Patrol security robot, and Cloud Pepper, a SoftBank Robotics humanoid. It has made them available through a robotics-as-a-service (RaaS) paradigm.
- Furthermore, ASORO labs of Singapore built a cloud computing infrastructure to generate a 3D model of the environment. This allows robots to perform simultaneous localization and mapping much faster than the labs' computers.


